
Perplexity AI is positioned as an “answer engine” (sometimes also described as a research assistant) that responds to a query with a natural-language answer plus citations to sources it used. (Perplexity AI)
● Goal: return a synthesized answer with verifiable references, rather than only a ranked list of links.
● Operationally: Perplexity says it searches the web in real time, then summarizes what it found.
Traditional web search (e.g., Google Search) is optimized to:
● retrieve and rank documents/pages,
● present them as links + snippets, and
● let the user do the synthesis.
Perplexity instead emphasizes:
● retrieving documents/snippets,
● compressing them into an answer,
● attaching citations to the supporting sources. (Search Engine Land)
A chatbot can answer from its model memory (training data) without necessarily showing where facts came from. Perplexity describes itself as retrieval-first: it uses web search and then generates an answer grounded in what it retrieved.
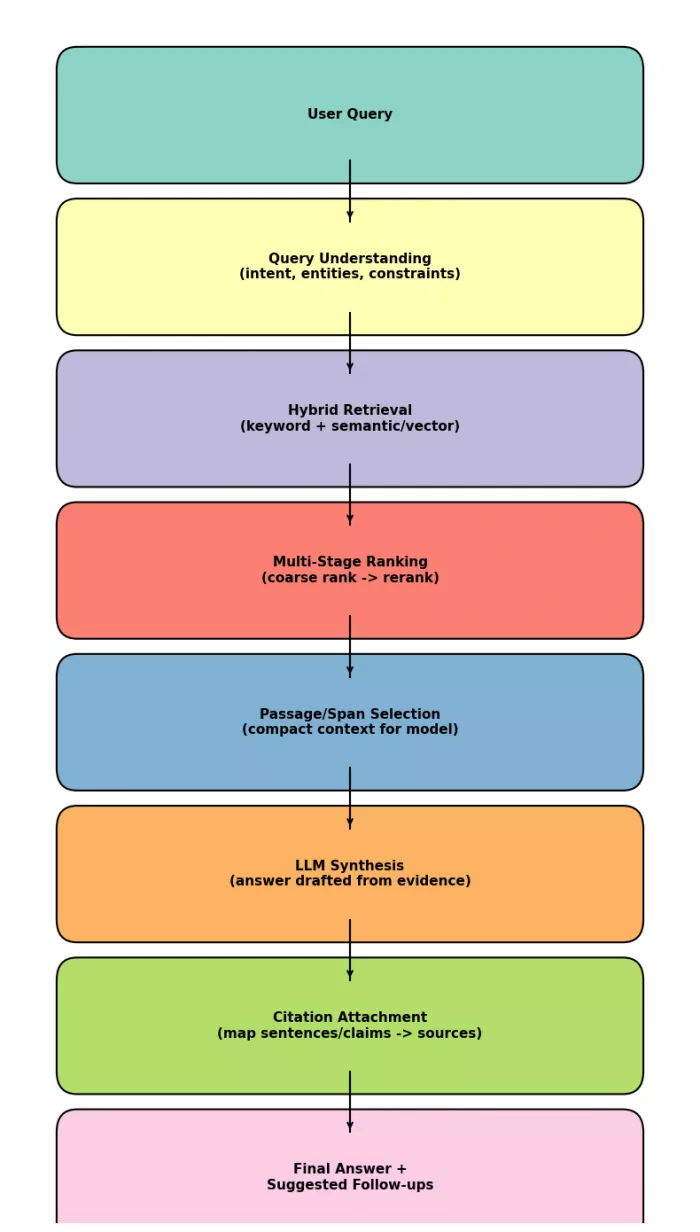
Perplexity’s public technical writing about its search infrastructure (especially the Perplexity Search API) gives a useful “inside” view of the key moving parts:
1. Query understanding:
○ The system analyzes the user query and intent (e.g., entities, constraints, desired freshness). Perplexity’s help center attributes this to “cutting-edge language models.”
2. Hybrid retrieval:
○ Perplexity describes an architecture with hybrid retrieval mechanisms (typically meaning a combination of lexical/keyword retrieval and semantic/vector retrieval), backed by large-scale indexing.
3. Fine-grained context selection:
○ A notable technical design point: it emphasizes not only document-level retrieval, but also treating sections/spans of documents as first-class units for “context engineering” (choosing the tightest, most relevant passages).
4. Multi-stage ranking:
○ Retrieved candidates are refined through multi-stage ranking pipelines.
○ Practically, this often looks like: fast initial retrieval → reranking with heavier models/signals → pick top passages for the final answer.
5. Citations:
○ The citations you see are tied to the retrieved sources/passages that were fed into the generation step (not simply “added later”). Perplexity’s product framing repeatedly emphasizes “answers with sources.”
● Retrieval systems (indexing + search + ranking) decide what evidence is likely relevant and trustworthy enough to include.
● Large language models (LLMs) turn the selected evidence into a coherent answer (summarize, reconcile conflicts, explain). Perplexity’s help center explicitly describes LLMs as part of query understanding and answer construction.
● Perplexity’s developer docs also separate “Search” use cases (retrieve + synthesize) from heavier reasoning tasks—suggesting different model modes depending on the job.
At a high level, grounding is achieved by:
● retrieving sources,
● selecting the most relevant passages,
● providing those passages to the LLM as context,
● generating an answer that is expected to stay consistent with that context,
What it is: a trace from the answer back to the retrieved documents/passages.
How it’s enabled: the retrieval layer supplies URLs (and often snippets/spans) that are inserted into the LLM prompt/context; the UI then displays the corresponding sources as citations. This design is consistent with Perplexity’s retrieval-first description and its emphasis on span-level “context engineering.”
What it is not: a guarantee that every sentence is perfectly supported; it’s a provenance signal that still requires checking (see limitations).
Perplexity behaves like a conversational system: follow-ups are typically handled by:
● carrying forward the prior turn’s topic constraints (entities, timeframe),
● running a new retrieval with the refined query,
● synthesizing again with new citations.
This is implied by its “answer engine” conversational workflow and retrieval-first approach.
Perplexity’s help documentation states it searches the internet in real time for answers.
Separately, Perplexity’s Search API article frames “staleness vs latency” as a core systems problem and describes building infrastructure to keep results usable for systems “hoping to be accurate and trustworthy.”
Perplexity’s developer documentation describes Search-type models as tuned for retrieval + synthesis, and notes they are not ideal for exhaustive multi-step analyses. (Perplexity)
Also, Perplexity’s help center names specific frontier models it may use for understanding and answering (as a product statement).
There are two different “performance” questions people often mix:
Perplexity published benchmark results for its Search API using an open-sourced evaluation framework and a set of benchmarks it lists (e.g., SimpleQA, FRAMES, BrowseComp, HLE). It reports:
● median latency (p50) around 358 ms (requests from AWS us-east-1), and
● comparative benchmark scores versus other search APIs in their test setup.
This is useful, but note it is vendor-published evaluation (good transparency, but still not fully independent).
| Platform | Rating |
| G2 | ~4.5 / 5 stars based on 135 reviews |
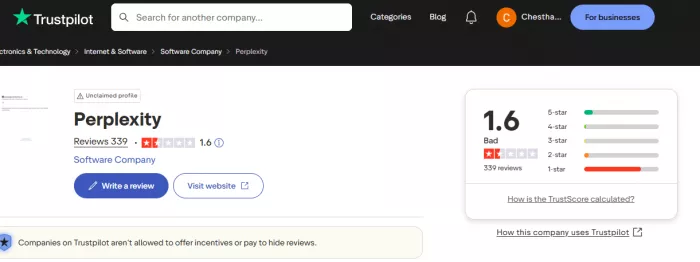
| Trustpilot | ~1.6 / 5 stars based on 339 reviews |
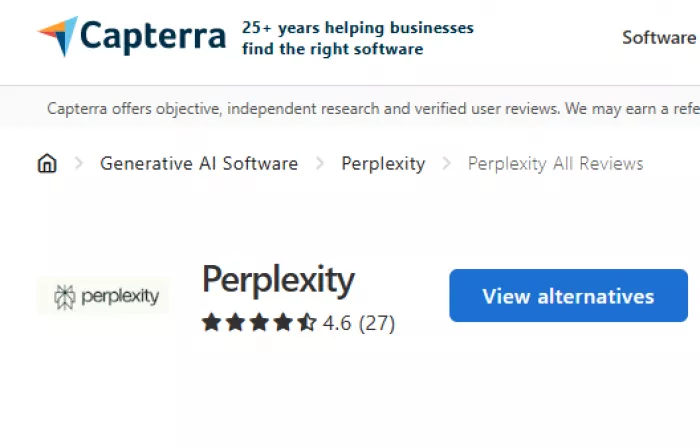
| Capterra | ~4.6 / 5 stars based on 27 reviews |

1. Strong Research Support & Source Attribution:
● Many verified reviewers appreciate Perplexity’s ability to produce answers with citations, aiding research and fact-checking.
● Users specifically value its utility in academic tasks (coding help, project work).

2. Easy to Use:
● Several comments highlight a clean, intuitive interface that makes it approachable even for complex queries.
3. Productive for Research Workflows:
● Some users say the tool runs in the background and helps gather information efficiently for longer research work.
1. Performance & Responsiveness Issues
● Users report very slow answers or responses that fail to meet expectations.
2. Poor Customer Support
● Frequent complaints about delayed or unhelpful responses from support staff.
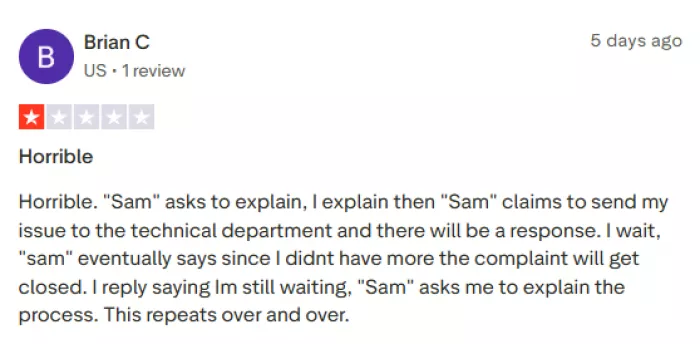
3. Subscription / Billing Problems
● Several reviews allege issues with unauthorized charges or difficulty canceling paid plans.
4. Inconsistent Output Quality
● Some reviewers claim the model drifts off in answers or remains incorrect despite corrections.
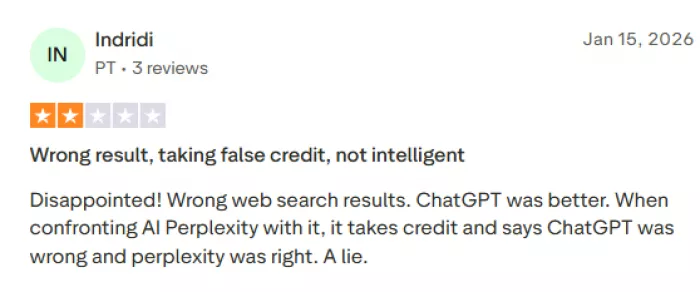
● Fact-finding with verification: when you want an answer and quick access to sources for checking.
● Rapid multi-source summaries: “What’s the consensus across sources?” style questions.
● Decision support with evidence: comparing options where citations let you inspect assumptions.
● Open-ended creative writing (citations don’t help much; retrieval may distract).
● Tasks requiring guaranteed correctness (medical dosing, legal advice, safety-critical steps): citations help auditing, but the model can still mis-synthesize.
● Very broad “exhaustive research” unless you can iterate: Perplexity’s own model docs caution that retrieval+synthesis modes aren’t ideal for exhaustive multi-step research by default.
| Dimension | Perplexity AI | Google Search (classic) | ChatGPT-style assistant (no browsing) |
| Primary output | Synthesized answer + citations | Ranked links + snippets | Generated text from model memory |
| Default grounding | Retrieval-first + cited sources (as positioned) | Grounded in documents (you read them) | Not grounded unless you provide sources/tools |
| Strength | Fast “answer with sources” workflow | Comprehensive index; best for navigating many results | Reasoning, drafting, transformation, brainstorming |
| Weakness | Can still misattribute/overgeneralize from sources | User must do synthesis; AI summaries vary by feature set | Can be outdated; may hallucinate without sources |
| Freshness | Claims real-time web search | Strong freshness for indexed web | Depends on training cutoff unless browsing/tools |
| Transparency | Citations expose provenance | Full transparency via links, but no synthesis guarantee | Often opaque unless it cites provided sources |
| Best use cases | Research summaries, quick fact checks, source-backed explanations | Deep dives, shopping, local results, broad exploration | Writing, planning, tutoring, coding, structured reasoning |
Perplexity AI is a retrieval-first answer engine that combines web search with an LLM to produce summarized answers with citations. Unlike Google Search (links) or ChatGPT-style tools (often no sources), it follows a pipeline like query understanding → hybrid retrieval → ranking → passage selection → LLM synthesis → citation attachment.
Public feedback is split: it scores high on G2 (~4.5/5) and Capterra (~4.6/5) for research and citation-backed summaries, but much lower on Trustpilot (~1.6/5) due to complaints about billing/support and inconsistent output. Overall, it works best for fast fact-finding and source-based summaries, but can still fail when sources are weak or when accuracy must be guaranteed.
Discussion